Continuous spinning of mof nanoparticules, a composite fiber material that unlocks the full potential of mofs
Domains
Environenment
Energy
Technology Advanced and active materials
Challenges
- High costs: Particularly the organic ligands used in MOF synthesis and the industrial process
- Stability issues: Degradation in the presence of water, over time, and at high temperatures.
- Scale-up difficulty: Achieving large-scale production with consistency remains a challenge.
Innovative solution
The integration of MOFs into a fibrous composite form, particularly using alginate as the matrix material, is the innovative solution. It combines the adsorption efficiency of MOFs with the flexibility and strength of fibers, making it suitable for large-scale production and a variety of practical applications, without compromising the porous structure of the MOFs.
Applications
- Gas storage and separation.
- Liquid purification.
- Electrochemical energy storage.
- Catalysis.
- Air Purification
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
Our invention overcomes these challenges by developing MOF-alginate composite fibers using a scalable spinning process. The alginate does not block the pores of the MOFs, ensuring high adsorption efficiency while offering the added benefit of being a bio-sourced polymer.
This solution also enhances the structural integrity and usability of MOFs in industrial applications.
How it works
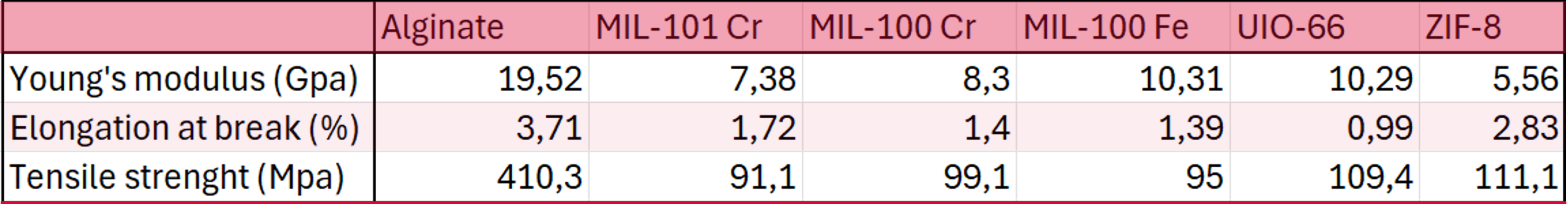
Several MOFs were synthesized to study the coagulation parameter with alginate. For this, the MOFs are dispersed in a solution of alginate and water, and fibers are produced through an extrusion process. Tensile tests are then conducted on these fibers to determine the elongation at break, tensile strength, and Young's modulus.
CHARACTERISTICS - TRL 3
Inventors
Renal BACKOV: CRPP (CNRS, university of Bordeaux)
IP
Patent filed in 2022
PARTNERSHIPS
License
Contact
Carlos Larraya
%63%2e%6c%61%72%72%61%79%61%40%61%73%74%2d%69%6e%6e%6f%76%61%74%69%6f%6e%73%2e%63%6f%6d
+33 (0)6 18 40 63 51